Natural arthritis remedies are holistic, non-pharmaceutical interventions designed to reduce joint inflammation, improve mobility, and manage chronic pain. These evidence-based strategies, detailed on our Home page, primarily include adopting an anti-inflammatory diet, utilizing potent supplements like curcumin and omega-3s, applying topical botanical analgesics, and engaging in low-impact movement therapies such as Tai Chi.
The Anti-Inflammatory Diet Protocol
The foundation of any natural approach to managing arthritis lies in nutrition. Chronic inflammation is the driving force behind the pain and stiffness associated with both osteoarthritis (OA) and rheumatoid arthritis (RA). By altering your biochemical environment through food, you can significantly dampen the inflammatory response.
Research consistently points to the Mediterranean diet as the gold standard for joint health. This eating pattern prioritizes whole foods rich in antioxidants, which neutralize free radicals that damage joint tissue.

Foods to Embrace
To proactively manage pain, your diet should be rich in the following:
- Fatty Fish: Salmon, mackerel, sardines, and trout are high in Omega-3 fatty acids, which inhibit the production of substances that cause inflammation (cytokines and enzymes).
- Cruciferous Vegetables: Broccoli, Brussels sprouts, and cabbage contain sulforaphane, a compound that helps slow cartilage damage in joints.
- Berries: Strawberries, blueberries, and raspberries are packed with anthocyanins, potent antioxidants that reduce inflammatory markers.
- Extra Virgin Olive Oil: Contains oleocanthal, which has an effect similar to non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs).
Inflammatory Triggers to Avoid
Equally important to what you eat is what you avoid. Certain foods can trigger an immune response that exacerbates joint pain:
- Processed Sugars: Excessive sugar intake triggers the release of cytokines.
- Refined Carbohydrates: White bread and pastries fuel the production of advanced glycation end products (AGEs), which stimulate inflammation.
- Omega-6 Fatty Acids: While necessary in small amounts, an excess of Omega-6s (found in corn, sunflower, and soybean oils) relative to Omega-3s can promote inflammation.
Powerhouse Supplements for Joint Health
While diet is paramount, getting therapeutic doses of specific compounds often requires supplementation. However, the supplement market is unregulated, making it crucial to choose evidence-based remedies.
Curcumin (Turmeric)
Turmeric is perhaps the most well-researched natural remedy for arthritis. Its active compound, curcumin, blocks inflammatory cytokines and enzymes, including cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2), the same target as the drug Celebrex.
Because curcumin is poorly absorbed by the body, look for supplements that include piperine (black pepper extract) or use phytosome technology to enhance bioavailability. Clinical trials have shown that high-quality curcumin supplements can be as effective as ibuprofen for knee osteoarthritis pain with fewer side effects.
Boswellia Serrata (Frankincense)
Boswellia Serrata, also known as Indian Frankincense, has been used in Ayurvedic medicine for centuries. It works by blocking the 5-LOX enzyme, another pathway of inflammation that NSAIDs typically do not target. This makes Boswellia a perfect partner to Curcumin. Similarly, Connecting with Mātauranga Māori (Māori Knowledge) for Health provides essential insights into integrating indigenous wisdom into modern wellbeing. Research suggests that Boswellia extracts can improve pain and physical function in osteoarthritis patients within as little as seven days.
Omega-3 Fatty Acids
If you cannot consume fatty fish three times a week, a high-quality fish oil or algal oil supplement is essential. The key components, EPA and DHA, compete with arachidonic acid in the body, effectively reducing the fuel available for the inflammatory fire. For therapeutic benefits, aim for a combined EPA/DHA dosage of at least 2,000 mg daily, though you should consult a healthcare provider before starting high-dose regimens, especially if you are on blood thinners.
For more detailed information on dietary supplements and safety, refer to the National Center for Complementary and Integrative Health (NCCIH).
Topical Treatments and Natural Analgesics
Topical remedies offer the advantage of delivering pain relief directly to the affected joint without the systemic side effects associated with oral medication. These are particularly effective for superficial joints like the knees and hands.

Capsaicin
Derived from chili peppers, capsaicin depletes substance P, a neurotransmitter that sends pain signals to the brain. Initially, application causes a burning sensation, but with regular use, it desensitizes the nerve endings. Over-the-counter creams containing 0.025% to 0.075% capsaicin are widely available and effective for osteoarthritis pain.
Arnica Montana
Arnica is a popular homeopathic remedy often used in gels and creams. While the mechanism is not fully understood, studies indicate that Arnica gel can provide pain relief comparable to ibuprofen gel for hand osteoarthritis. It helps reduce bruising and swelling, making it a gentle option for those with sensitive skin. For broader homeopathic support, see our guide on Oscillococcinum: Flu Symptom Management.
Movement Therapies: Tai Chi and Yoga
The adage “motion is lotion” is scientifically accurate regarding joint health. Synovial fluid, which lubricates the joints, requires movement to circulate effectively. Sedentary behavior causes this fluid to stagnate, leading to stiffness and increased degeneration.
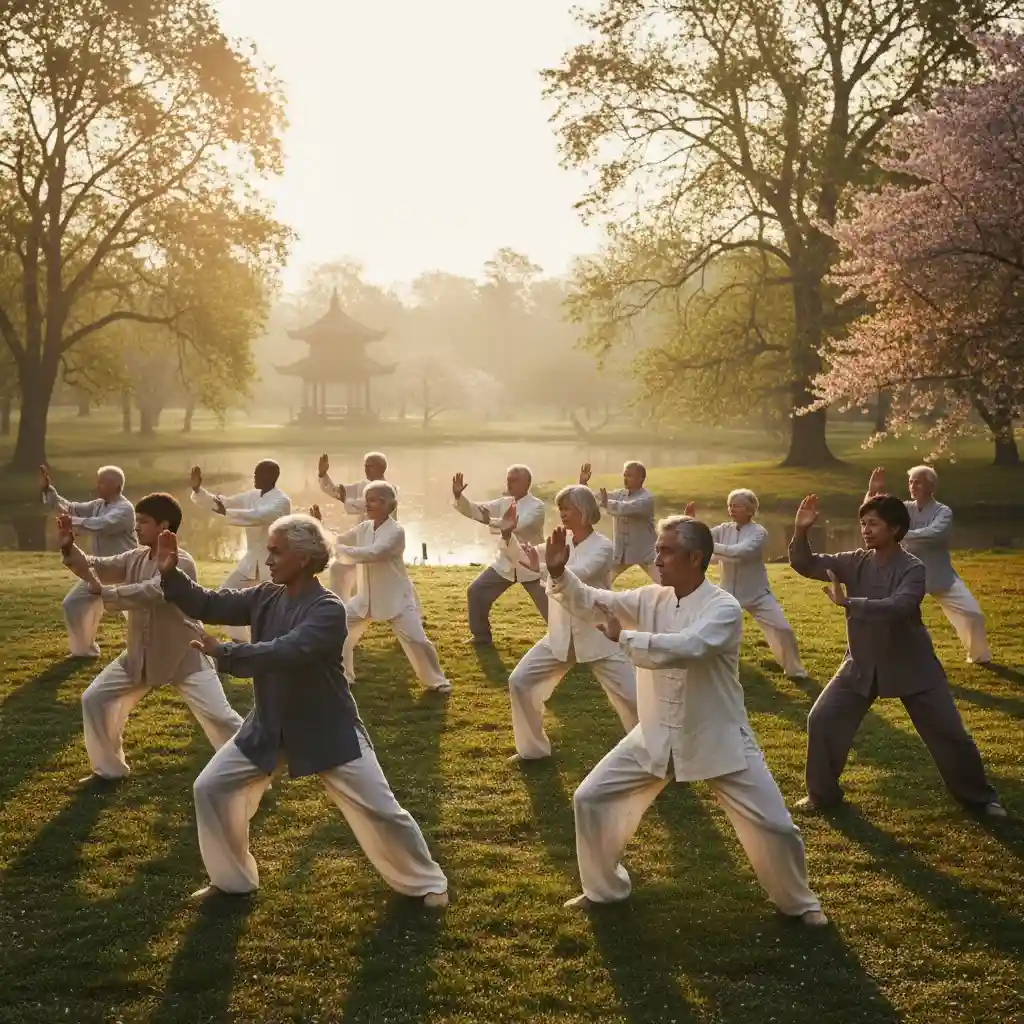
The Benefits of Tai Chi
Tai Chi is a Chinese martial art that involves slow, controlled movements and deep breathing. It is exceptionally beneficial for arthritis patients because it improves balance, strength, and flexibility without high impact on the joints. According to the Arthritis Foundation, Tai Chi has been shown to significantly reduce pain and improve physical function in people with knee osteoarthritis.
Yoga Modifications for Arthritis
Yoga helps maintain range of motion and strengthens the muscles surrounding the joints, providing better stability. However, standard yoga poses may need modification. Iyengar yoga, which uses props like blocks and straps to ensure proper alignment, is often recommended. Avoid “hot yoga” if you have inflammatory arthritis like RA, as extreme heat can sometimes trigger flare-ups in certain individuals.

Mind-Body Approaches and Lifestyle Factors
Managing arthritis is not just about the physical body; it involves the nervous system and how the brain processes pain. Chronic pain can sensitize the central nervous system, making pain signals louder.
Acupuncture
Acupuncture involves inserting thin needles into specific points on the body to stimulate the nervous system. The World Health Organization recognizes acupuncture as helpful for over 100 conditions, including osteoarthritis. It is believed to stimulate the release of endorphins (natural painkillers) and influence the autonomic nervous system to reduce inflammation.
Weight Management
Mechanical stress is a major contributor to joint degeneration. For every pound of body weight lost, there is a four-pound reduction in knee joint load for each step taken. Combining the anti-inflammatory diet with low-impact movement naturally supports weight management, creating a positive feedback loop that reduces pain and slows disease progression.
People Also Ask
What is the strongest natural anti-inflammatory for arthritis?
Curcumin, the active compound in turmeric, is widely considered the strongest natural anti-inflammatory. When combined with piperine (black pepper) for absorption, it rivals the effectiveness of some NSAIDs by blocking inflammatory pathways like COX-2.
How can I lubricate my joints naturally?
To lubricate joints naturally, stay hydrated, consume healthy fats (Omega-3s from fish, avocado, olive oil), and engage in regular movement. Supplements like Glucosamine and Chondroitin may also support the maintenance of cartilage and synovial fluid.
Does apple cider vinegar help with arthritis?
While anecdotal evidence suggests apple cider vinegar (ACV) may help due to its anti-inflammatory properties and pectin content, there is currently limited scientific evidence specifically linking ACV to arthritis pain relief. However, it is generally safe to consume in moderation.
What foods trigger arthritis pain?
Common triggers include processed foods, refined sugars, excessive red meat, fried foods, and refined carbohydrates. Some individuals also report sensitivity to nightshade vegetables (tomatoes, peppers, eggplant), though this varies by person.
Can arthritis be reversed naturally?
Arthritis damage, particularly the loss of cartilage in osteoarthritis, cannot typically be fully reversed. However, natural remedies can halt progression, significantly reduce symptoms, and in some cases, allow the body to repair minor damage, leading to a largely pain-free life.
Is heat or cold better for arthritis pain?
It depends on the symptoms. Heat therapy (warm baths, heating pads) helps relax muscles and lubricate joints, making it best for stiffness. Cold therapy (ice packs) reduces swelling and numbs deep pain, making it ideal for acute inflammation or flare-ups.